System Architecture
The System Architecture of our end-to-end test incorporates a platform cluster.
Platform Cluster
The platform cluster consists of five Namespaces:
control-plane: constitutes the core of the platform. Its purpose is to build the connection to the external applications, to provide API endpoints, and to ensure that data transactions are properly initiated and managed through restricted workflow-templates. It acts as a central point of control for managing data access and usage and consists of multiple microservices which are described below.transaction-plane: initiates the transaction-workflow using the provided workflow-templates via Argo Workflows, an open-source container-native workflow engine for orchestrating parallel jobs on Kubernetesdata-plane: hosts the temporary databases for each transaction, as well as the associated workflow and the workflow-template which will be provided by the external user. The registration process of these workflow-templates is managed by thetransaction-service.base: Keycloak provides the IAM and monitoring functionalities.prometheus: Prometheus is an open source metrics monitoring tool.
Services
Transaction Service
The transaction-service offers the possibility to start and end the transaction and to start the app workflow.
Functions
- endTransaction
- startTransaction
- startWorkflow
- getWorkflow
- findTransaction
- getAllTransactionIds
Messaging Service
The messaging service is responsible for handling message exchanges between services using HTTP-based messaging.
Functions
- postMessage
- getMessages
Credential service
This service is responsible for the creation and management of the database credentials.
Functions
- createRoleExternal
- createRoleInternal
Database service
This service creates and deletes the transaction and safe deposit databases.
Functions (transaction database)
- createRolesForDatabase
- createTransactionDatabase
- deleteRolesForDatabase
- deleteTransactionDatabase
Functions (safe-deposit database)
- createSafeDepositDatabase
- deleteSafeDepositDatabase
App service
This service offers the possibility to find or delete an app, get all app IDs or start the app registration.
Functions
- deleteApp
- findApp
- getAllAppIds
- startAppRegistration
Eurodat Client
This client offers the possibility to start or end a transaction or to start a workflow.
Functions
- endTransaction
- startTransaction
- startWorkflow
- getWorkflow
Contract service
This service offers the possibility to create, find, or terminate a contract or to get all contracts and the health status.
Contract creation is based on businessID.
The businessID is composed of contractType userSubject.
For every businessID, there can only be one currently valid contract.
A contract is said to be valid, if its validTo is in the future and validFrom is in the past.
As well as its validity, we store the status of each contract.
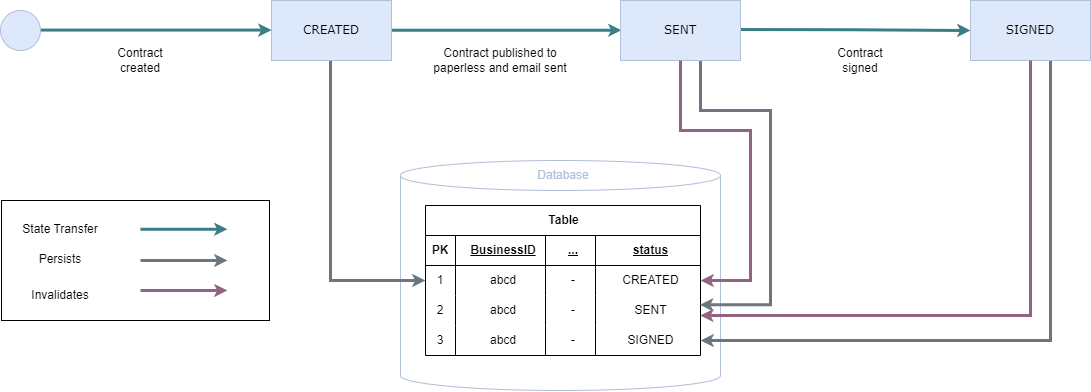
The status of a contract is one of CREATED, SENT, or SIGNED.
For the sake of auditability, we store all previous versions of contracts, whenever a contract is changed.
This means that for any field (other than validTo) changing it is done by terminating the old contract (by setting validTo=now) and creating
a new contract with the updated parameter.
For example, let's say we have a contract with status SENT.
When this contract is signed, we set the validTo of the current contract ot now.
We then create a new contract which is a clone of the old one, but with status=SIGNED.
The following figure represents the transition between statuses and its effects on the database.
Functions
- createContract
- findContract
- getAllContracts
- terminateContract
